English I - Miss Rocío
martes, 27 de junio de 2017
Idioms! - Animals
Look at these idioms with animals! Try to understand their meaning and we'll talk about them next class. Have a great day!
Monthly Planner!
Here goes the monthly planner for July. Please, check it before every class so you know what we are going to learn or revise.
domingo, 25 de junio de 2017
viernes, 23 de junio de 2017
Revision!
These are all the things that you should already know. In this board, you will find links to the explanations so you can click on the title and check them if you have any doubt. Also, there are some links to exercises that will help you practice the tenses.
miércoles, 21 de junio de 2017
Meet Peter and understand the present!
If you have doubts about the use of the Present Simple and Present Continuous, It would be a great idea to watch this video. You'll find it very easy to understand. 😃
lunes, 19 de junio de 2017
Time expressions - Present Simple and Continuous
Use the Present Simple with:
- Always, usually, sometimes, often, never: I always do the shopping on Saturday.
- On + days: On Fridays, I go out for dinner.
- Whenever: Whenever I'm hungry, I count to ten.
Use the Present Continuous with:
- Now: They're doing some housework now.
- Currently: Currently, we are living in England.
- At the moment: I'm not working at the moment.
sábado, 17 de junio de 2017
Present Simple vs. Present Continuous
- Present Simple: Routines, facts, planned events in the near future, instructions.
Affirmative sentence: Subject + verb (+s) + the rest of the sentence.
Negative sentence: Subject + do not/ does not + main verb in the infinitive form + the rest of the sentence.
Yes/No Question: Do/Does + subject + main verb in hte infinitive form + the rest of the sentence.
Examples: He plays tennis.
She doesn't like going to the supermarket on Sundays.
Do you study tenses regularly?
- Present continuous: An action taking place at the moment of speaking.
Affirmative sentence: Subject + verb to be in the present (am/is/are) + main verb with -ing + the rest of the sentence.
Negative sentence: Subject + am/is/are not + main verb with -ing + the rest of the sentence.
Yes/No Question: Am/is/Are + subject + main verb with -ing + the rest of the sentence.
Examples: He is playing tennis right now.
She isn't studying at the moment.
Are you cleaning the bathroom? No, I am having a shower now.
viernes, 16 de junio de 2017
miércoles, 14 de junio de 2017
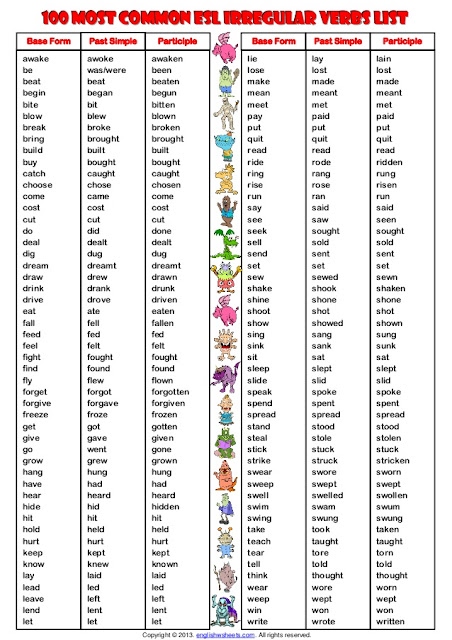
Irregular verbs
Many English verbs are regular, which means that they form their different tenses according to an established pattern.
For example: Laugh: Laughs (3rd person singular present tense), laughed (past tense)
There are many irregular verbs that don’t follow the normal rules. Here are the forms of the most common irregular verbs. Please, have a look at them and try to study them.
If you want to practice regular and irregular verbs, click here.
For example: Laugh: Laughs (3rd person singular present tense), laughed (past tense)
There are many irregular verbs that don’t follow the normal rules. Here are the forms of the most common irregular verbs. Please, have a look at them and try to study them.
If you want to practice regular and irregular verbs, click here.
 |
lunes, 12 de junio de 2017
Mixing the tenses! - Past simple and Past continuous
We often use the past continuous and the past simple tenses together. When this happens, the past continuous describes a longer, ‘background’ action or situation and the past simple describes the action or events.
- When I woke up this morning it was raining and my father was singing in the kitchen.
- I was walking home, whistling happily, when I saw two masked men run out of the bank.
Often, the ‘action’ described by the past simple tense interrupts the ‘situation’ described by the past continuous tense.
- I broke my leg when I was skiing.
- I was playing a computer game when the doorbell rang.
Notice that the past continuous describes ‘situations’ that go on for some time – ‘skiing’ and ‘playing’ but the past simple describes ‘actions’ that happen quickly – ‘broke’ and ‘rang’.
Notice too important differences between these two sentences:
Notice too important differences between these two sentences:
- When they arrived, Jeff was cooking dinner. ➔ Jeff started cooking before they arrived.
- When they arrived, Jeff cooked dinner. ➔ Jeff started cooking dinner after they arrived.
Time expressions - Past Simple and Continuous
Use the Past Simple with:
- Ago: I saw that film two weeks ago.
- Last: Last month, I was on holiday.
- When: When did you see him? I saw him when I was in London.
- Then: I finished my work, then I drove home.
Use the Past Continuous with:
- While: I lost my wallet while I was walking home.
- When: I was having a shower when the phone rang.
- During: During the summer, I was working on a farm.
Past Simple vs Past continuous
Did you do it or were you doing it?
- PAST SIMPLE: A completed action in the past.
Structure of the sentence: Subject + verb (+ed) + the rest of the sentence.
Negative sentence: Subject + didn't + verb in the infinitive form + the rest of the sentence.
Yes/No question: Did + subject + verb in the infinitive form + the rest of the sentence.
- PAST CONTINUOUS: An action that was taking place at some point in the past.
Structure of the sentence: Subject + verb to be in the past (was/were) + main verb with -ing + the rest of the sentence.
Negative sentence: subject + wasn't or weren't + main verb with -ing + the rest of the sentence.
Yes/No question: was/were + subject + main verb with -ing + rest of the sentence.
Welcome!
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)






